Razzi's guide to php
Install php:
$ sudo apt install php
There’s also a helpful tool here: https://www.php.net/downloads.php
Create an index.php file:
<?php
echo "hi"
?>
You can serve a single directory:
$ php -S localhost:8000
[Fri Aug 15 17:05:02 2025] PHP 8.4.0RC1 Development Server (http://localhost:8000) started
Open in your browser http://localhost:8000.
Yippee!
Hit control-c to stop the php development server.
Running php with apache server
Now let’s make it part of an apache site so you can view your site without having to worry about starting a server manually.
Edit /var/www/html/index.php.
Since it is in a directory owned by root, you need sudo permissions to edit it.
sudo vi /var/www/html/index.php
Add the following contents:
<?php
echo phpinfo()
?>
Access http://localhost/index.php this time.
You should see a phpinfo page like the following:
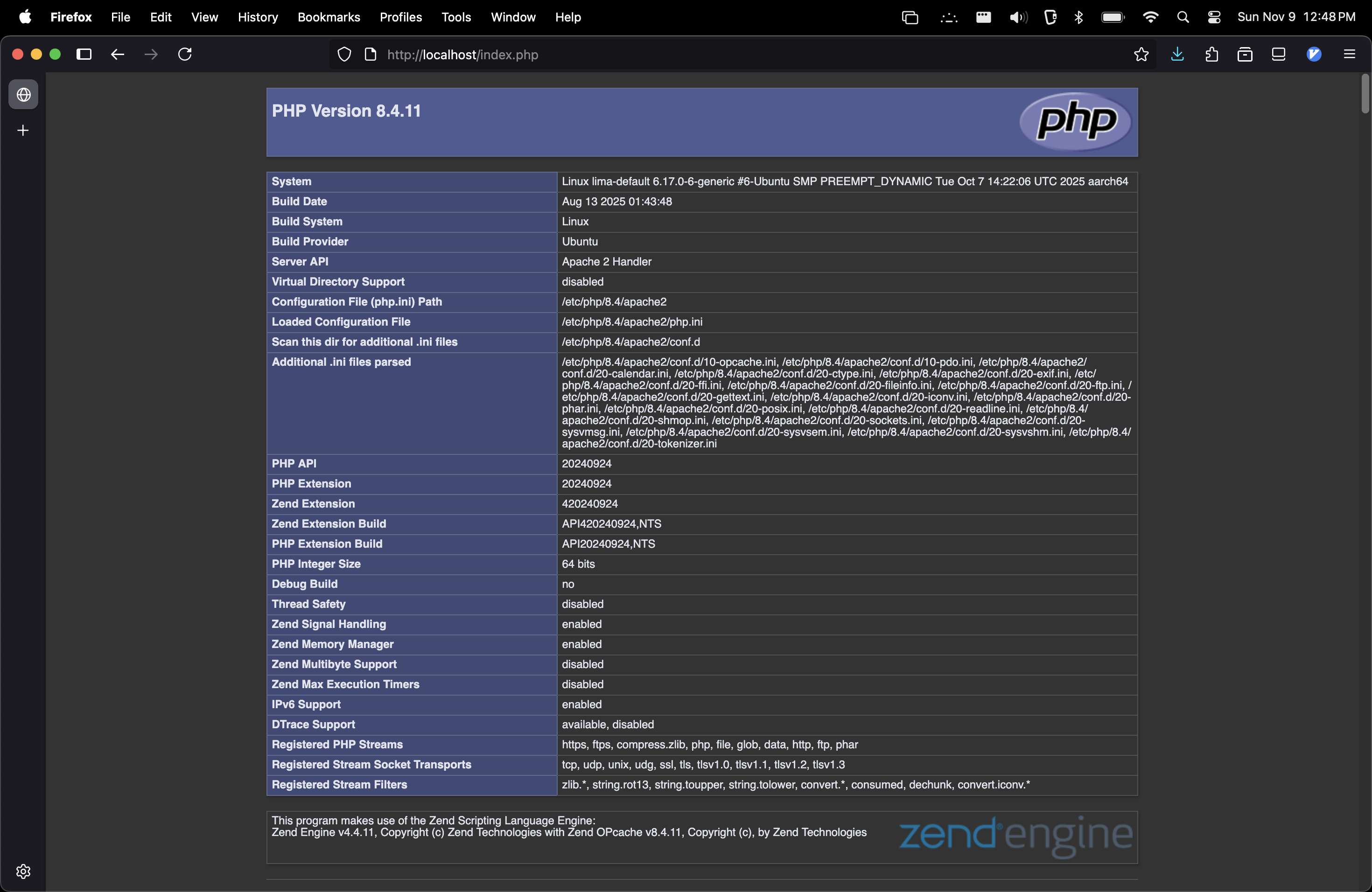
Allowing edits without sudo
A better approach here is to make a second site that points to a directory your user can edit.
First make a directory in a location that php can see, like /srv/mysite:
$ sudo mkdir /srv/mysite
$ sudo chown $(whoami) /srv/mysite
# Put some content in the index so you know if your site is being served:
$ echo 'hello world' > /srv/mysite/index.php
Then you have to add apache configuration for your new site.
I decided to put my development site on port 5000.
To create a new apache site, create a new file in the /etc/apache2/sites-available/ directory:
sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/001-mysite.conf
Listen 5000
<VirtualHost *:5000>
DocumentRoot /srv/mysite
<Directory /srv/mysite>
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Now enable the site with a2ensite and reload like it tells you to:
$ sudo a2ensite 001-mysite.conf
Enabling site 001-mysite.
To activate the new configuration, you need to run:
systemctl reload apache2
$ sudo systemctl reload apache2.service
$
Open your browser to http://localhost:5000 and everything should be working.
If you run into a Forbidden error, check your access logs:
$ sudo tail /var/log/apache2/error.log
If you run into a configuration error (such as a syntax error), check the apache service logs:
sudo journalctl -xeu apache2.service
You could just edit the existing site and use sudo, but by creating a new site you can keep your files files in /srv/mysite, separate from the default files, and edit without sudo.